Innovative Tool Material Solutions for Stamping, Trimming, Fine Blanking and other metal forming applications by ROVALMA
Stamping, trimming and fine blanking of metals which use plastic deformation below the metal’s recrystallization point to shape the metal into the desired parts are some of the most common metal forming applications that are frequently also grouped under the term of cold work metal forming operations. Other applications that fall into this category of material forming operations are: drawing, sheet shear cutting, deep drawing, extrusion and bending, amongst others.
The selection of the most advantageous tool material for a given cold forming operation is a key factor for optimizing product quality and the cost-effectiveness of the production process. When selecting a tool material for a given forming application, it is hence decisive to select the tool material taking the diverse requirements resulting from a specific production configuration into account. Some of the most important variables to be considered are: the characteristics of the metal to be formed, the main tool failure mechanisms occurring in a given forming operation, and the resulting requisites regarding the property requirements to be satisfied by the tool material. Typical tool failure mechanisms in metal forming operations are:
- Adhesive wear: the metal to be shaped or the coating applied to it adheres to the tool surface, often causing a decrease of clearance and premature tool failure. Tool materials that enable improved surface finish or substrate properties for coatings can frequently help in tackling this problem.
- Abrasive wear: hard particles contained in the metal to be shaped can cause abrasive wear on the tool surface. This problem can often be mitigated by an increase of the hardness level of the tool material or by fine-tuning of the tribological properties of the tool material.
- Chipping: which is a low cycle fatigue failure mechanism that usually appears after a low number of strokes - tool material of the active tool edge breaks and chips off. Increasing the tool material’s toughness can help resolving this problem.
- Fatigue: this phenomenon describes tool failure under cyclically applied load values that are lower than the tool material's yield strength.
- Plastic deformation: typically causes tool failure when the active edge of the tool suffers plastic deformation due to a lack of the tool material’s compression strength.
- Accidents: tools can break occasionally because of unforeseen accidents related to specific operation conditions.
For high-duty applications, such as for example the forming of advanced high and ultra-high strength steels (AHHS, UHHS) with mechanical strength beyond 700 MPa and up to 1600 MPa, long production serious or other demanding production configurations, the used tool materials have to combine many properties, typically high mechanical strength, high hardness, compression resistance, toughness and high wear resistance that allow to withstand severe working conditions. Conventional standard tool steels are often not up to this job. In view of increasingly restrictive environmental and safety regulations, the use of AHSS and UHSS has been dynamically growing in the transport industry, where these materials enable lightweight construction with improved crash performance. Nowadays, advanced high strength steels are estimated to represent about 20 – 25 % of the vehicle weight, while it is forecasted that their use will increase to about 70% - 80% within the next decade.
At ROVALMA, we have set our tool material design targets for cold metal forming applications in creating solutions that provide the following main advantages:
- Increase tool durability
- Reduce maintenance costs
- Increase part quality through the reduction of burr
- Reduce the cutting stresses on the component to prevent delayed fracture
- Increase part quality of the sheared edge
Because different application configurations require different mechanical and tribological properties, we have optimized our grades accordingly:
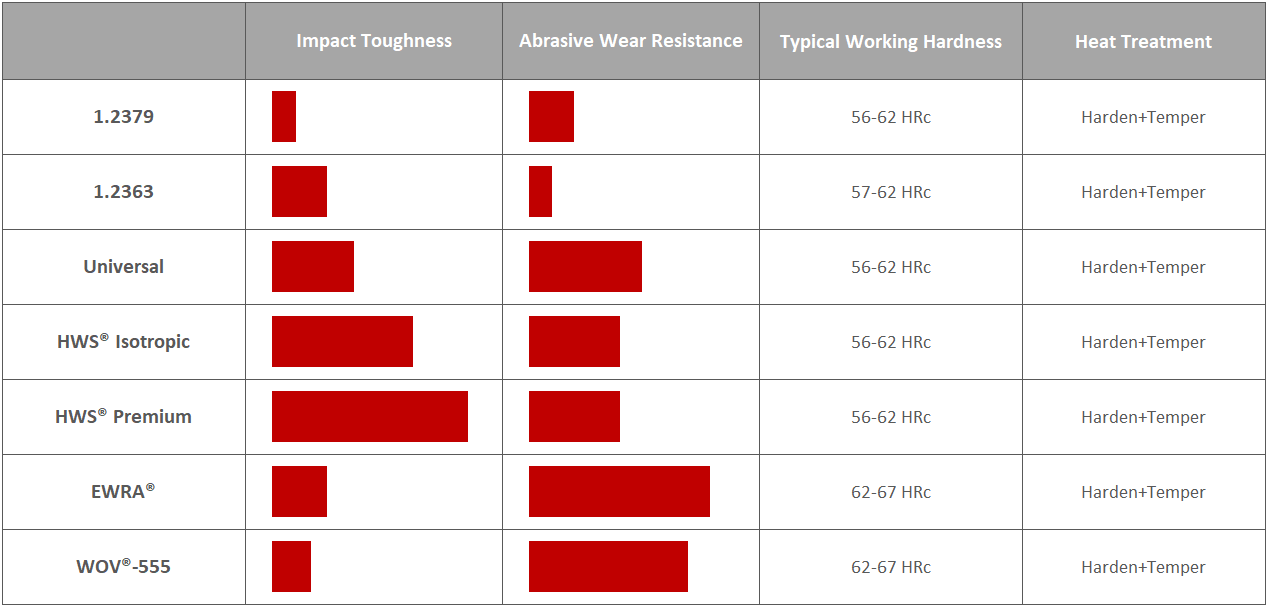
For more information, please refer to the corresponding technical material data sheet or contact our Applications Engineering Department by phone or email: ae-fast@rovalma.com.
